We could approach the traditional job description of Rev Man or Revenue Manager. However, with this article we want to give a clearer idea of what is the day-to-day life of this professional and all his team. Its most strategic role within the organization is structuring. This is a recent job in the Portuguese reality, which a few years ago did not have such important label for business units viability and growth.
The Revenue Manager job description may vary from propriety to propriety, depending on its structure and goals or propriety type. Usually these are multipurpose professionals and the area where they operate requires knowledge that goes far beyond traditional hotel management.
They are true "Wizards", since for outsiders, the magic happens based on innumerable factors that these professionals master. For others it is almost the fruit of occult and magic potions based on statistical calculation.
This is responsible for the preparation, implementation of the strategy and procedures for revenue creation in the hotel, using various practices and growth techniques. Identifies opportunities based on a constant market study, with all its elements (competitors, customers, etc.). It is responsible for optimizing the distribution and sale of the hotel, analyzing production per channel with intrinsic knowledge of the costs involved. It is the expert that through analysis of historical data and comparison with forecast, creates the best strategy for getting the best price, at the best time, to the right customer, the best possible offer for a future date.
In a revenue management team, in more complex structures, we can observe several functions organized according to the level of experience of their performers. Below we can see several designations, being the entry position in the company as "Yield Analyst" and the position that requires more experience as "Corporate Director of Revenue Management". All the tasks of the revenue management department are performed by these professionals and all are fundamental, and these are divided by the different functions according to their degree of responsibility or technical knowledge.
Key roles in Revenue Management departments:
• Yield Analyst
• Junior Revenue Manager
• Market Revenue Manager
• Cluster Revenue Manager
• Senior Area Revenue Manager
• Director of Revenue Management
• Corporate Director of Revenue Management
This position is so crucial, that it is increasingly common to see these professionals sitting at the table in board meetings, reporting directly to it and directing other departmental teams such as Marketing, Sales, commercial or operational teams. This is simple to understand , any decision of a Revenue Manager or his team directly affects the revenue generated by the hotel. The hotel positioning must be in line with the revenue strategy. It is intended, therefore, that in addition to an excellent revenue manager, this manager is also a human asset manager, in order to build a team, with a single direction oriented towards the same common objective. In this last point, the reality is quite different and we are still far from the practices already adopted in other international markets.
However, it is desirable for Board members and the CEOs to place the RM team in an autonomous position so that it can create the needed synergies to influence all other departments and their revenue optimization habits.
But the market data show that this is the trend and these departments are increasingly gaining notoriety and relevance.
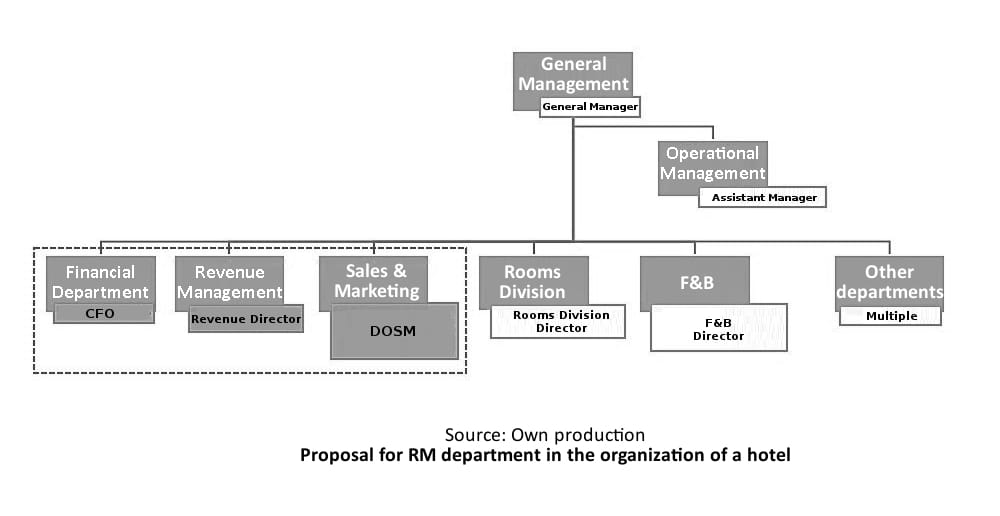
Integration of the RM department into the organizational structure:
There is a HSMAI study that showed that in most of the hotels surveyed, 36% of these Revenue Managers reported to the General Manager, 23% to another departmental director (DOSM or Rooms Division Director), 16% to the Board Vice President, 16% to the RM Regional Director and 9% to the CEO. What we can observe is that in more mature companies these professionals are more autonomous reporting directly to the General Manager or directly to the Board. There is a consensus in the industry that these professionals should be as autonomous as possible, so we understand that this department, in the limit, should be at the level of the propriety main departments, reporting directly to the general management or Board, working in tune directly with the finance department (CFO), Marketing and Sales (DOSM). Otherwise, these departments should level up above all others and report directly to the Board or General Management of the propriety.
The 10 pillars of the revenue optimization process:
Its main functions go from developing strategies for optimizing revenues for the hotel or other accommodation units, based on the main 10 pillars of revenue creation.
These 10 pillars are as diverse as:
- Diagnosis
- Demand Stimulation
- Demand Forecasting
- Short-term operational management (overbookings, no-shows and cancellations)
- Sales price management (pricing and segmentation)
- Displacement analysis (groups)
- Inventory Management
- Distribution (channel management and distribution costs)
- Reputation management (online and offline guest feedback)
- Evaluation (efforts of revenue management actions)
These professionals work closely with the marketing, sales, commercial, reservations, or front-office teams, reporting directly to the board or chief executive officer. They are highly specialized, constantly attentive to market changes and multiple actions by their competitor group, adjusting the offer based on these external data and the company's internal response capability with the available resources for a given moment.
General Duties and Responsibilities:
In order to achieve the desired revenue optimization for the hotel or other accommodation propriety within the hotel and tourism industry, this professional should perform the following tasks:
1. Monitor all hotel revenue
The hotel structure should be properly organized, with accounts assigned to the various revenue generating centres. It is essential to have budgeting per department, as well as allocation of the corresponding cost centres. The entire computer system and its tools should be parameterized for a sustained analysis of correct data. In this way, the RM will be able to calculate the revenue generated by nature/outlet . With the information generated, he should suggest corrections and optimize revenue in line with the existing accounting system.
2. Create Pricing strategies and make price management
This is undoubtedly the main challenge of the Revenue Manager, this task is nothing more than determining and establishing the rates to practice in order to make the hotel competitive and create revenue. Sales price management and segmentation are preponderant factors in the revenue optimization dynamics, thus deep customer knowledge becomes fundamental.
3. Constant competition and demand analysis
The environment where the hotel is located and its competitive group is a factor that influences the definition of competitive prices and the hotel performance. This professional will have to identify demand and sector trends, defining the market segments to bet on, which future events and changes in the economic scenario can positively or negatively affect the propriety.
4. Preparation, production, monitoring of performance reports and forecast production
As this professional works directly with the top management, it is up to him to prepare all the intelligible information on the propriety performance. These reports will highlight the difficulties for future dates (forecasts) as well as solutions for minimizing the impact and maximizing revenue (for example, marketing campaigns or preparation of charm offensives carried out by commercial departments, etc.).
Core skills of a Revenue Manager:
Such a multidisciplinary position obliges a professional with varied characteristics within the organizational sphere.
We emphasize the following:
- Creative Thinking
- Excellent analytical and mathematical ability to deconstruct data quickly
- Master communication skills, whether customer service, meetings or reporting.
- Strong relational skills
- Born sellers
- Strong ability in team management
- Attention to detail as well as ability to prioritize revenue generation over time-consuming and non-productive tasks.
- Ability to deal with stressful situations
- High level of motivation, determination and commitment
- Result-oriented
- Operational experience (hotel)
- Strong skills for team building
- Advanced user of computer systems
- Database and Excel knowledge
- Expert in digital marketing
- Knowledge, interpretation of financial statements and P&L
- Management background
- Focused on goals
- High confidence and technical skills in Revenue Management
How are divided the functions of a Revenue Management team?
The permanent monitoring of external and internal data to carry out the adopted strategy leads to the organization of the functions at 5 frequency levels (daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly and annual), which can be adjusted according to the Revenue Management team as well as the company where it is inserted and its structure dimension (being more or less complex). However, this systematized frequency is a critical success factor when implementing an efficient strategic optimization of total revenue (THRMO) system. Only in this way can Revenue department teams clearly identify who, what, when and how revenue management tasks need to be executed quickly.
We suggest a distribution of tasks as follows:
-
Daily
- It is recommended, at the beginning of the day, to analyze the pick-up of hotel reservations. This pick-up report will indicate the reservations fluctuations made from the previous day to the present, for the next 14 days.
- Analyze the prices of our competitors for the next 14 days through tools like Rate Shoppers, as well as dates on which they have no availability.
- Review hotel rates based on the above collected information. Adjust rates and discounts if needed (Early Bookings % discount).
- Review the "House Status", overbookings for the next 14 days (increase or decrease rates according to established)
- Review rates restrictions for the next 3 months (LOS, CTA, etc.), when applied.
- Based on the PMS reports, we should analyze the performance of the last night based on the indicators (OCC, ADR, RevPAR , etc.), compared to the budgeted.
- Analysis of the groups pick-up and MICE segment in the last 24 hours for the next 14 days. Act in accordance with the previously analysed.
- Reputation Management of social networks, using specific platforms for this purpose (online and feedback forms available to guests).
-
Weekly
- Review pick-up from the last 24 hours for the next 3 months.
- Analysis of Competitive Set prices for the same period (3 months), as well as dates with lack of availability.
- Based on the above mentioned reports, adjust rates, promotions and restrictions for the same period (Early Bookings % discount).
- Review the "House Status", overbookings for the next 90 days (increase or decrease rates according to established)
- Check overbooking situations for the next 3 months according to unit strategy. Adjust if necessary.
- Review all content of the hotel on the website (CMS) and OTA's, making sure that it is updated accordingly.
- Manage channels according to its production, availability and associated distribution costs (OTA's and Soft Brands). Confirm your most popular dates and close the rates for Early Bookings, discounted rates or Opaque when justified.
-
Monthly
- Review pick-up from the last 24 hours to the end of the inventory.
- Manage inventory for the end of inventory period.
- Compare "Comp Set" rates to the end of inventory as well as dates with no availability (Rate Shopper).
- Review and adjust, if necessary, all rates, restrictions and discounts (BAR and EB % discount).
- Review Overbooking levels for the end of inventory.
- Review RM reports, based on history, analyzing trends, to confirm that all actions are as planned, adjust if necessary. Analyze for the next 12 months, which are the most searched dates in order to adjust inventory, rates and/or restrictions (LOS and CTA).
- Analyze revenue by distribution channel, comparing the associated costs (net revenue per distribution channel).
- Meet with the general management and departmental managers to discuss the sales strategy, forecasting, demand, OTB business, overbooking, sales mix, STR results, up-selling and cross-selling strategy, etc... in order to engage in the strategy, the GM, DOSM, FBM, Reservations Manager and Rooms Division Manager must be present to direct them towards the same objective.
-
Quarterly
- Full analysis of content in all locations (OTAs, TA, Web, TO, etc.), update information and photos.
- Review sales strategy through product configuration checks and mappings.
- Complete audit of OTAs, comparison of net production with global revenue and content update.
-
Yearly
- Renegotiate contracts with operators, companies, OTAs , etc., based on production, weight on hotel revenue and respective distribution costs.
- Budget definition and revenue strategy based on historical data and future trends (choose the most appropriate method).
- Meet with reservations department staff, analyze their production and bet on a visit to familiarize themselves with the propriety.
- Redefining the Comp Set (parameters and new competitors)
- Preparation of annual forecasts
Final considerations
The professionals of RM, are professionals with a high degree of attention to detail, capacity of analysis and the deconstruction of data is fundamental to the position of Revenue Manager. A large roll of skills is expected from this set of professionals, these bear the responsibility of each action for the production of additional revenue. It is desirable that these professionals be increasingly independent of other departments, reporting directly to general management or the Board. The growth and viability of the company as well as other jobs depend on these professionals. It is easy to conclude that, in the near future, these professionals will be more autonomous, with a strong emphasis on the organizational structure, having a transversal influence throughout the organizational structure related to the production and optimization of revenues. In order to carry out all this management these professionals use a set of tools, which will be addressed in a next article.



